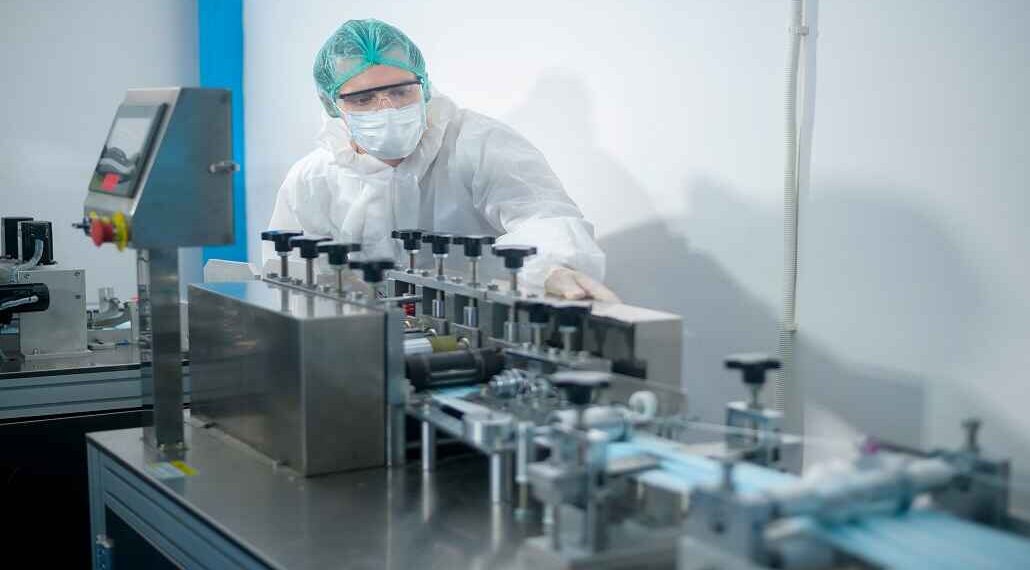
In the recent years that have gone by, the pharmaceutical sector has gone on to see significant progress, thereby generating a novel set of biotherapeutics and also biosimilars at a rate that’s unprecedented. It is worth noting that one of the biggest challenges in the sector is to come up with high-quality biologics and that too in flexible volumes and, at the same time, decrease the cost just so that the access to potentially lifesaving biological treatment improves substantially. Manufacturers are hence consistently looking out for groundbreaking approaches so as to push their development and also production processes so as to meet the growing as well as diversifying demands.
It is well to be noted that batch and also fed-batch systems for long have been effective when it comes to biotherapeutic manufacturing with advances that push yields of almost 10g/l. But the traditional fed-batch manufacturing systems happen to struggle to keep pace with the ever-rising demands in production.
Besides, dynamic conditions found within the bioreactor can very well lead to an imbalance as far as nutrient supply as well as waste accumulation is concerned, thereby resulting in glycosylation that’s incomplete and also compromised cell health, in addition to higher degradation of the product. All this would obviously lead to affecting the product quality to a large extent. Also, the low volumetric productivity when it comes to fed-batch biotherapeutic manufacturing also needs to have some large facilities that go on to raise the cost of production.
The Transition to Consistent Manufacturing
The transition from traditional batch as well as fed-batch methods to a much more resource-led and efficient, automated, as well as continuous, manufacturing process goes on to offer biopharma companies a very convenient solution so as to prominently enhance their quality of the product and also the overall productivity.
In quite a contrast to the batch methods, continuous processing happens to maintain balanced conditions in the bioreactor, thereby offering a continuous supply when it comes to fresh nutrients along with continual eradication of waste so as to support high cell densities along with growth phases that are extended. All this goes on to lead to better productivity, which in more ways than one exceeds the fed-batch systems limits and also enhances the process efficiencies. In a way, simpler and more cost-effective media formulations can get used for the ongoing turnover of media, thereby making sure of a total process economics that’s pretty much improved. Moreover, continuous manufacturing also goes on to bring the added advantage of higher flexibility in case of biopharmaceutical manufacturing since it helps production in smaller plants that happen to be amenable to modular design as well as are more readily responsive when it comes to fluctuations in the market demands.
It is worth noting that there are many companies that are already capitalizing on these advantages and, at the same time, converting them so as to leverage cost of production for the later stages when it comes to commercial manufacturing and also biopharmaceutical manufacturing and its development. Interestingly, continuous biomanufacturing can as well be hybrid, semi-continuous, or completely end-to-end. Hybrid manufacturing happens to combine batch and continuous processing in a single production workflow. For instance, upstream processes, capture of the product, and also viral inactivation can run consistently, whereas subsequent polishing purification steps happen to be batch even if they happen to be very highly intensified.
Hybrid manufacturing gets often applied across the early phase of clinical manufacturing, when the priority, as far as sponsors are concerned, is generating material in case of toxicological studies and also first-in-human clinical trials in the shortest time possible. A hybrid process can very well freely be converted to a more absolute end-to-end process in the later stages but before phase III clinical trials. Hybrid manufacturing may as well be favored before end-to-end methods since they happen to need less automation and can, as a matter of fact, be established in a swifter way. On the other hand, semicontinuous manufacturing workflows happen to be less efficient as compared to end-to-end setups and hence never deliver overall productivity perks when it comes to a completely continuous processing.
End-to-end manufacturing makes use of a completely integrated and continuous workflow that covers all steps right from cell culture to the final product purification, which means that there happens to be a consistent flow of materials throughout the overall production chain so as to maximize the efficiency. A completely end-to-end continuous manufacturing platform enables making sure of the highest returns, manufacturing footprints that are small, and the highest standards of quality while at the same time curtailing the risk of scaling up the processes and also decreasing the cost of goods. All these strengths go on to mean that end-to-end continuous manufacturing happens to be gaining a lot of speed in the leading biopharma companies that seek a lower-cost production method and also a competitive edge.
Throttling Productivity Teamed with Processes that are Intensified
Intensified cell perfusion cultivation happens to be an advanced bioprocessing technique that is designed to amplify the cell growth and also product yield in the biomanufacturing gamut. It enables consistent feeding when it comes to fresh media and at the same time eradicates spent media, therefore resulting in cell densities that are high, constant viability, and also better quality of the product when it comes to continuous manufacturing workflows. Also, advanced process controls as well as analytical tech that are used in intensified cell perfusion cultivation enable maintaining conditions that are consistent in the bioreactor. Experts when it comes to perfusion processes happen to be capable of directly amping up these cultures from -3 to 500- or 1000-liter bioreactors apt for both commercial and clinical applications. This helps with a seamless shift from process development into late-stage manufacturing as well as commercial supply.
Mixing this continuous processing that’s intensified with a highly productive cell expression system can help with high titers in terms of biotherapeutic material that often exceeds 4 g/l/day and also offers manufacturers more opportunities so as to refine the varied quality attributes of their respective candidates. Better host productivity as well as throughput also enables a decrease in the footprint of the facility needed to generate a similar volume of the end product, thereby helping with production to take place within the modular clean rooms, which can in a way be swiftly installed within existing facilities or even constructed separately by way of using parallel techniques of construction. The smaller facility footprint further goes on to lower the total cost when it comes to therapeutic protein manufacture, therefore making it possible to attain a COG of less than $50/g in some cases, which is 75% less than the present industry benchmark.
To Sum It Up
Biopharmaceutical manufacturing can go on to dramatically enhance their product outcomes as well as quality by way of switching from a batch, fed batch or even hybrid manufacturing process to a more complete end-to-end continuous workflow. These efficiency gains can as well be multiplied by way of adopting a perfusion cell culture process that’s intensified as well as a highly productive cell expression system. The fact is that the end-to-end continuous manufacturing happens to have the capacity to very much lower the cost of manufacturing and offer options to decrease the price of biosimilars and also biologics so as to make sure of wider access to these kinds of necessary therapies.