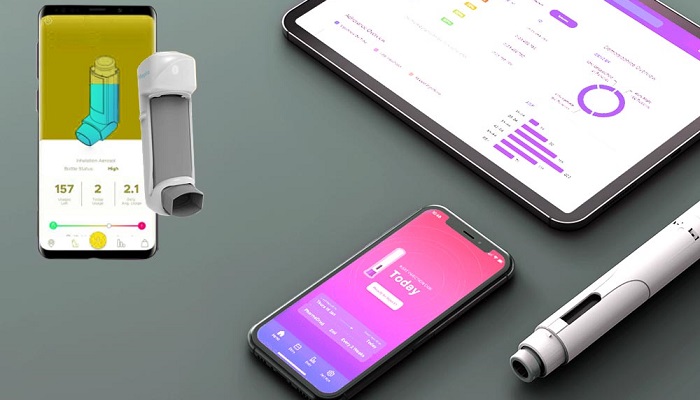
The market for connected drug delivery devices is anticipated to witness a growth rate of almost 23.4% every year from 2022 to 2030. The value of the category is expected to touch $25.6 billion by 2030.
This quick expansion happens to be pushed by trends that lie both within and outside the healthcare segment: the elevated adoption of the IoT by way of smarter devices that have sophisticated sensors as well as processing capacity, a progressive acknowledgment that applying contactless health services makes the efficiency robust, and the move towards smarter, consumer-friendly devices monitoring health metrics.
The introduction of digital features across medical products happens to be a logical step in the scenario of such trends, but there are also both commercial and healthcare incentives. As the sector continues to progress and elevate, let us look into what the connected device market is looking to achieve in the years to come and how it is likely to push enhanced adherence to treatments, thereby benefiting entire health outcomes.
Given the current trends that happen to be part of drug development, the manufacturing of drug delivery devices that provide users with detailed instructions at each step of the injection experience is very important. Besides rapid moves from intravenous to subcutaneous administration, drug formulations are indeed changing as firms look to lessen the disruptions to the lives of patients by broadening the time between two injections. Some release formulations that are extended help patients go longer between treatments; in some scenarios, it is even more than 6 months. With patients using these devices less regularly, there is a greater need for crystal-clear guidelines throughout the injection process.
The connected devices can go on to provide real-time and in-use feedback to patients to guide them through each step when it comes to using this device. This enables them to reduce errors within the injection process in the case of self-administration, which can lead to an incomplete as well as a failed dosage. Apart from this, training devices that happen to have advanced sensors that allow individualised and specific guidance as compared to those who are using the device for the very first time can also lead to elevated patient confidence as well as successful administration. They can also be termed a reassuring support tool for those who happen to be switching devices.
Apart from the guidance that the patients get from their devices, the injection data is set to be a seamless process for patients. At present, the most connected devices come tagged along with a smartphone application that one has to download to have data access, like the reminder for injections. That said, with the advent of 5G, one would be able to see device data being uploaded directly to the cloud without even having to have devices or secondary applications. This will help in the real-time transfer of data, thereby allowing health officials to remotely track the treatment without even needing any kind of input from the patients.
It is well to be noted that applications are most likely to take a back seat with the data being transferred by the cloud to the apps for patients only if they wish.
Numerous amounts of data can be taken and stored by way of connected drug delivery devices, like detailed real-time data when it comes to date, time, site, and dosage, as well as the drug confirmation and expiration date of the injection. These can be tagged with other sources of data to provide an entire view of the patient’s health and to better gauge special treatment requirements. Physiological data like BP and heart rate, as well as lifestyle data like exercise and sleep habits, can now be seamlessly captured and tracked consistently because of wearable devices like smartwatches. Making use of the data collected from them in sync with the drug delivery device’s data can indeed prove valuable when it comes to triggering required patient interventions and thereby enhancing healthcare results.
Across healthcare settings, what has been observed thus far is limited interoperability, which is the capacity of the computer systems when it comes to exchange as well as making use of data and its integration. This is, however, starting to change because of the increased focus on remote patient monitoring. It is well to be noted that providers are now witnessing the benefits that data integration can bring when it comes to better healthcare results.3 As and when an entire picture of patients gets developed by way of multiple sources of data, healthcare experts would ideally be able to come up with the right treatments or regimens that are customised as per every patient. This is likely to elevate adherence when it comes to treatment plans, build a healthier population, and, at the end of the day, reduce commercial strain on payers as well as healthcare systems.
The key data on how the patient is using the device, for example, the angle at which the device is being held or the amount of force being applied, can also be collected as and when the clinical trials are conducted by using connected devices. This can be used to support the data that gets accumulated during human factor studies, thereby providing evidence that patients happen to be using only those devices needed during the clinical trials. After the launch, the data can be used to pinpoint and take care of any user challenges and also enable root cause analysis.
The information, notably, can also be passed to the device manufacturers, who can function on the usability issues and gauge if the design alterations may be essential in the case of certain groups of patients. All this means that the data that is gradually collected from the drug delivery devices that are connected will go on to play a crucial role in enhancing the device itself and finally providing an elevated experience to the patients.
With the connected device market growing at a rapid pace and many manufacturers wanting to be a part of it, there happens to be an increased list of designs in the devices as well as their configurations for pharma companies and also patients to opt from, right from single-use as well as reusable devices to add-on or integrated connectivity. It is well to be noted that the opinions on the options that are regarded as the best are consistently changing since wireless technology and the performance of varied electronic components continue to evolve. Commercial arguments are also making a shift as regulations evolve quite quickly and considerations about sustainability keep growing in importance.
With major differences when it comes to pathways concerned with regulatory nods as well as environmental benchmarks, the ideal option in one market may not be a great one in another.
Because of the numerous changing elements, pharma companies are looking for flexible drug platforms, and understandably so. Devices that can have varied fill volumes are more attractive; for example, innovations like self-adjusting plungers Devices that can work with or without connectivity can be useful for pharmaceutical companies as they help with flexibility, which is based on patient group preferences or the status of reimbursement across various healthcare markets.
The capacity to opt either for single-use or reusable devices is also crucial for pharma companies that happen to be looking for apt device manufacturers. Going forward, these varied avenues should lead to an array of device options that happen to be different, which will mean that more options will be available both for patients and for pharma companies.
The fact is that the growth in the drug delivery market in the years to come is most likely to lead to enhancements across several areas. Patients will go on to have access to devices that happen to be more user-friendly, thereby helping them to be more at ease during the time of self-administration as well as improving the process of injection.
Furthermore, the ability of the devices to upload the data directly to the cloud will aid in optimising the data collection process, thereby allowing for a real-time transfer of data without any manual input from the patients. As more data gets gathered on how patients would be using devices and where issues happen to be occurring, manufacturers will be able to make changes to the device to meet the requirements of varied patient groups.
This, in turn, will go on to provide many options for patients, who are, by the way, already benefiting from the many sources that happen to be emerging from a connected drug delivery device market that’s growing.
REFERENCES
- GrandView Research. Connected Drug Delivery Devices Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Product, By Route Of Administration (Parenteral, Inhalational), By Application (Asthma, COPD, Diabetes Management, Others), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2023 – 2030. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/connected-drug-delivery-devices-market.
- GrandView Research. Connected Drug Delivery Devices Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Product, By Route Of Administration (Parenteral, Inhalational), By Application (Asthma, COPD, Diabetes Management, Others), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2023 – 2030. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/connected-drug-delivery-devices-market.
- Keith, J. et al. How better use of data can help address key challenges facing the NHS. https://www.health.org.uk/publications/long-reads/how-better-use-of-data-can-help-address-key-challenges-facing-the-nhs#:~:text=Good_use_of_data_is,evaluate_efforts_to_integrate_care Steventon, A. Helping the NHS use data better to improve patient care. https://www.health.org.uk/news-and-comment/blogs/helping-the-nhs-use-data-better-to-improve-patient-care.